Configure Update Orchestration¶
You can configure update orchestration using the Horizon Web interface.
About this task
The update orchestration interface is found in Horizon on the Patch Orchestration tab, available from Admin > Platform > Software Management in the left-hand pane.
Note
Management-affecting alarms cannot be ignored at the indicated severity level or higher by using relaxed alarm rules during an orchestrated update operation. For a list of management-affecting alarms, see StarlingX Fault Management: Alarm Messages. To display management-affecting active alarms, use the following command:
~(keystone_admin)]$ fm alarm-list --mgmt_affecting
During an orchestrated update operation, the following alarms are ignored even when strict restrictions are selected:
200.001, Maintenance host lock alarm
900.001, Patch in progress
900.005, Upgrade in progress
900.101, Software patch auto apply in progress
Prerequisites
You cannot successfully create an update (patch) strategy if any hosts show Patch Current = Pending, indicating that the update status of these hosts has not yet been updated. The creation attempt fails, and you must try again. You can use sw-patch query-hosts to review the current update status before creating a update strategy.
Procedure
Upload and apply your updates as described in Manage Software Updates (do not lock any hosts or use host-install to install the updates on any hosts).
Select Platform > Software Management, then select the Patch Orchestration tab.
Click the Create Strategy button.
The Create Strategy dialog appears.
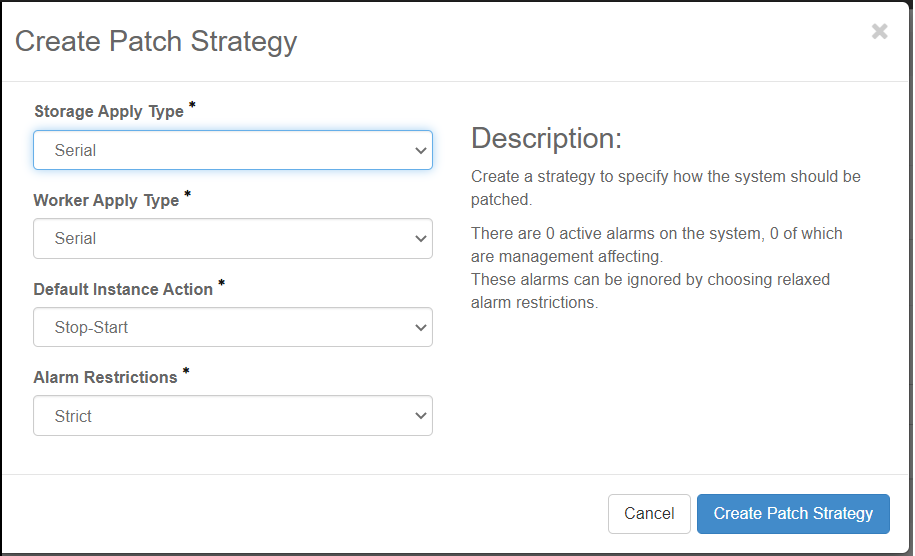
Create a update strategy by specifying settings for the parameters in the Create Strategy dialog box.
- Description field
Provides information about current alarms, including whether an alarm is Management Affecting.
- Controller Apply Type
Serial (default): controllers will be updated one at a time (standby controller first)
Ignore: controllers will not be updated
- Storage Apply Type
Serial (default): storage hosts will be updated one at a time
Parallel: storage hosts will be updated in parallel, ensuring that only one storage node in each replication group is updated at a time.
Ignore: storage hosts will not be updated
- Worker Apply Type
Serial (default): worker hosts will be updated one at a time
Parallel: worker hosts will be updated in parallel
At most, Parallel will be updated at the same time.
For a reboot parallel update only, worker hosts with no pods are updated before worker hosts with pods.
Parallel: specify the maximum worker hosts to update in parallel (minimum: 2, maximum: 100)
Ignore: Worker hosts will not be updated
- Default Instance Action
This parameter only applies for systems with the stx-openstack application.
Stop-Start (default): hosted applications VMs will be stopped before a host is updated (applies to reboot updates only)
Migrate: hosted application VMs will be migrated off a host before it is updated (applies to reboot updates only).
- Alarm Restrictions
This option lets you specify how update orchestration behaves when alarms are present.
You can use the CLI command fm alarm-list --mgmt_affecting to view the alarms that are management affecting.
- Strict
The default strict option will result in update orchestration failing if there are any alarms present in the system (except for a small list of alarms).
- Relaxed
This option allows orchestration to proceed if alarms are present, as long as none of these alarms are management affecting.
Click Create Strategy to save the update orchestration strategy.
Note
The update orchestration process ensures that no hosts are reported as Patch Status = Pending. If any hosts have this status, the creation attempt fails with an error message. Wait a few minutes and try again. You can also use sw-patch query-hosts to review the current update status.
Examine the update strategy. Pay careful attention to:
The sets of hosts that will be updated together in each stage.
The sets of hosted application pods that will be impacted in each stage.
The update strategy has one or more stages, with each stage consisting of one or more hosts to be updated at the same time. Each stage is split into steps (for example, query-alarms, lock-hosts, sw-patch-hosts). Note the following about stages:
Note
Controller hosts are updated first, followed by storage hosts and then worker hosts.
Worker hosts with no hosted application pods are updated before worker hosts with hosted application pods.
The final step in each stage is
system-stabilize, which waits for a period of time (up to several minutes) and ensures that the system is free of alarms. This ensures that the update orchestrator does not continue to update more hosts if the update application has caused an issue resulting in an alarm.
Click the Apply Strategy button to apply the update strategy. You can optionally apply a single stage at a time by clicking the Apply Stage button.
When applying a single stage, you can only apply the next stage; you cannot skip stages.
To abort the update, click the Abort Strategy button.
While a update-strategy is being applied, it can be aborted. This results in:
The current step being allowed to complete.
If necessary an abort phase will be created and applied, which will attempt to unlock any hosts that were locked.
Note
If a update strategy is aborted after hosts were locked, but before they were updated, the hosts will not be unlocked, as this would result in the updates being installed. You must either install the updates on the hosts or remove the updates before unlocking the hosts.
Delete the update strategy.
After a update strategy has been applied (or aborted) it must be deleted before another update strategy can be created. If a update strategy application fails, you must address the issue that caused the failure, then delete and re-create the strategy before attempting to apply it again.
