Deploy Edgeworker Nodes¶
Introduction¶
Edgeworker is a new node personality introduced in StarlingX R5.0 [[1]]. Edgeworkers are typically small systems running dedicated workloads that can now be managed by StarlingX. To use the edgeworker personality, nodes must have the Ubuntu operating system installed [[2]].
The edgeworker personality is targeted for nodes that meet one or more of the following criteria:
A node that is running a customized OS, or
A node that is running a Type1 hypervisor, or
A node that does not meet StarlingX worker’s minimum requirements.
These nodes can be added to a running StarlingX cluster in minutes. During the provisioning stage, Kubernetes components will be provisioned on the edgeworker nodes.
The StarlingX controller manages edgeworker nodes using the same mechanisms as typical worker nodes, including the following:
Container orchestration by Kubernetes
Distributed storage cluster management by Rook-ceph
Notes
Hardware Requirements¶
The minimum requirements for an edgeworker host (bare metal or virtual machine) are:
Minimum Requirement |
Edgeworker Node |
|---|---|
Minimum processor class |
Intel® Core™ Processor Family |
Minimum memory |
16GB |
Primary disk |
256GB SSD or NVMe |
Minimum network ports |
|
Prepare Edgeworker Nodes¶
Before you provision edgeworker nodes, you must prepare the following setup:
Deploy StarlingX AIO Duplex or Standard setup.
Connect the Edgeworker node to power and power it on.
Connect the Edgeworker node to the network and connect it to a management network switch.
Set the primary disk as the first boot device in the BIOS setting of the edgeworker node.
Install Ubuntu 18.04 (or above) on the edgeworker node.
Install Openssh-server and Python.
The figure below shows how edgeworker nodes are connected to an existing StarlingX cluster.
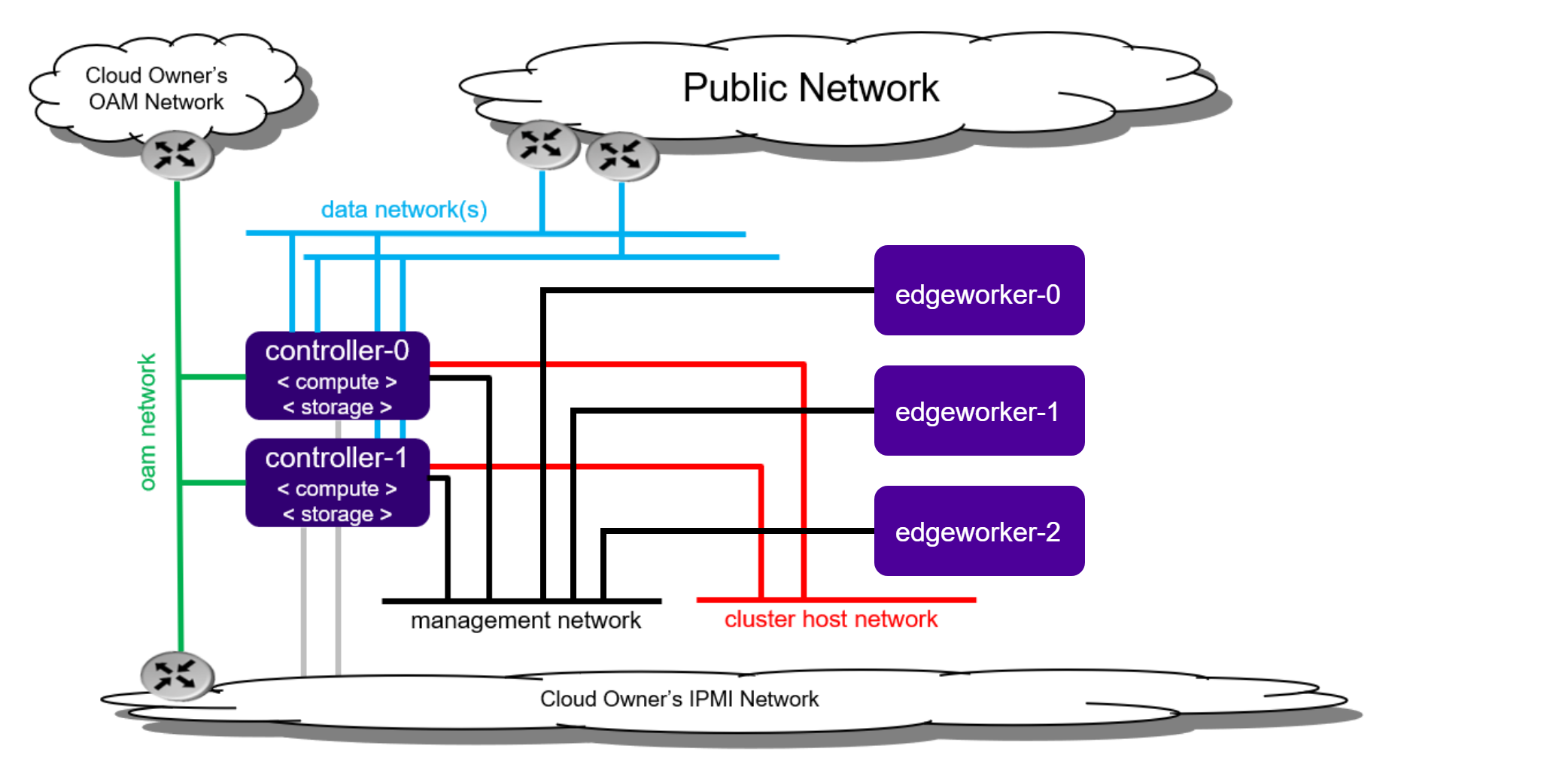
Provision Edgeworker Nodes¶
When a node’s network interface is connected to the management network switch, the node is detected and will appear in the list of hosts managed by system inventory (with personality set to None).
[sysadmin@controller-0 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-list
+----+--------------+-------------+----------------+-------------+--------------+
| id | hostname | personality | administrative | operational | availability |
+----+--------------+-------------+----------------+-------------+--------------+
| 1 | controller-0 | controller | unlocked | enabled | available |
| 2 | controller-1 | controller | unlocked | enabled | available |
| 3 | None | None | locked | disabled | offline |
+----+--------------+-------------+----------------+-------------+--------------+
Update the node’s hostname and personality using
system host-update:[sysadmin@controller-0 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-update 3 hostname=edgeworker-0 personality=edgeworker +-----------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +-----------------------+--------------------------------------+ | action | none | | administrative | locked | | availability | offline | | bm_ip | None | | bm_type | None | | bm_username | None | | boot_device | /dev/sda | | capabilities | {} | | clock_synchronization | ntp | | config_applied | None | | config_status | None | | config_target | None | | console | ttyS0,115200 | | created_at | 2021-02-05T02:12:42.136121+00:00 | | device_image_update | None | | hostname | edgeworker-0 | | id | 3 | | install_output | text | | install_state | None | | install_state_info | None | | inv_state | None | | invprovision | None | | location | {} | | mgmt_ip | 192.188.204.21 | | mgmt_mac | 52:54:00:76:e6:cb | | operational | disabled | | personality | edgeworker | | reboot_needed | False | | reserved | False | | rootfs_device | /dev/sda | | serialid | None | | software_load | nn.nn | | task | None | | tboot | false | | ttys_dcd | None | | updated_at | None | | uptime | 0 | | uuid | a2c8f3ec-1dc4-4a0a-b471-6e5c01abc187 | | vim_progress_status | None | +-----------------------+--------------------------------------+
Alternatively, if the node is not shown in the host list automatically, you can also add the host using
system host-add:[sysadmin@controller-0 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-add -n edgeworker-0 -p edgeworker -m <mgmt_mac>
Check the prerequisites of the edgeworker node:
Note
We suggest using the same username and password for all the edgeworker nodes.
EWUSER=<edgeworker username> EWPASSWD=<edgeworker password> SYSADMINPASSWD=<sysadmin password> EWNODE=(edgeworker-0) PYTHONBIN=() for NODE in ${EWNODE[@]}; do EDGEWORKER=$(system host-show ${NODE} | awk '/mgmt_ip/{print$4}'); PYTHONBIN+=($(sshpass -p ${EWPASSWD} ssh -o "StrictHostKeyChecking no" ${EWUSER}@${EDGEWORKER} which python)); done ERR=0 for i in ${PYTHONBIN[@]}; do if [ -z "$i" ]; then ERR=1 break fi done if [ $ERR == 1 ]; then echo "Error, python should be intalled on edgeworker nodes." else echo "Pre-requisites check passed." fi
If the following error occurs, refresh the DHCP client for the management interface on the edgeworker nodes to assign the right IP address.
ssh: connect to host XX.XX.XX.XX port 22: No route to host
Create an edgeworker inventory file with the variables from the previous step.
tee ./edgeworker_inventory.yml << EOF all: hosts: localhost: ansible_connection: local children: edgeworker: hosts: EOF for i in ${!EWNODE[@]}; do echo " ${EWNODE[$i]}:" echo " ansible_ssh_user: ${EWUSER}" echo " ansible_ssh_pass: ${EWPASSWD}" echo " ansible_become_pass: ${EWPASSWD}" echo " ansible_python_interpreter: ${PYTHONBIN[$i]}" done | tee -a edgeworker_inventory.yml tee -a ./edgeworker_inventory.yml << EOF vars: ansible_ssh_user: sysadmin ansible_ssh_pass: ${SYSADMINPASSWD} ansible_become_pass: ${SYSADMINPASSWD} EOFProvision the edgeworker node using Ansible playbook. You can provision edgeworker nodes one at a time or multiple nodes at once. Run the playbook with the inventory file you created.
ansible-playbook -i ./edgeworker_inventory.yml /usr/share/ansible/stx-ansible/playbooks/provision_edgeworker.yml
Provisioning output is similar to the following:
TASK [provision-edgeworker/prepare-edgeworker/kubernetes : set_fact] ********************************************************************************************************* ok: [edgeworker-0] TASK [provision-edgeworker/prepare-edgeworker/kubernetes : Pull k8s gcr images from controller registry to edgeworker-0] ***************************************************** changed: [edgeworker-0] RUNNING HANDLER [provision-edgeworker/prepare-edgeworker/kubernetes : Restart kubelet] *************************************************************************************** changed: [edgeworker-0] PLAY [localhost] ************************************************************************************************************************************************************* TASK [provision-edgeworker/prepare-controller/cleanup : Cleanup temporary files] ********************************************************************************************* changed: [localhost] TASK [provision-edgeworker/prepare-controller/cleanup : Remove the provision flag] ******************************************************************************************* changed: [localhost] PLAY RECAP ******************************************************************************************************************************************************************* edgeworker-0 : ok=54 changed=10 unreachable=0 failed=0 localhost : ok=31 changed=19 unreachable=0 failed=0
After provisioning, the edgeworker node will show
Readystatus in the Kubernetes cluster.[sysadmin@controller-0 ~(keystone_admin)]$ kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION controller-0 Ready master 42h v1.18.1 controller-1 Ready master 42h v1.18.1 edgeworker-0 Ready <none> 21m v1.18.1
Note
In StarlingX R5.0, the edgeworker nodes will be shown as
locked/disabled/offline when you use the system host-list command.
