Static VXLAN¶
The static unicast mode relies on the mapping of neutron ports to compute nodes to receive the packet in order to reach the VM.
In this mode there is no multicast addressing and no multicast packets are sent from the compute nodes, neither is there any learning. In contrast to the dynamic VXLAN mode, any packets destined to unknown MAC addresses are dropped. To ensure that there are no unknown endpoints the system examines the neutron port DB and gathers the list of mappings between port MAC/IP addresses and the hostname on which they reside.
Static VXLAN is limited to use on one data network. If configured, it must be enabled on all OpenStack compute nodes.
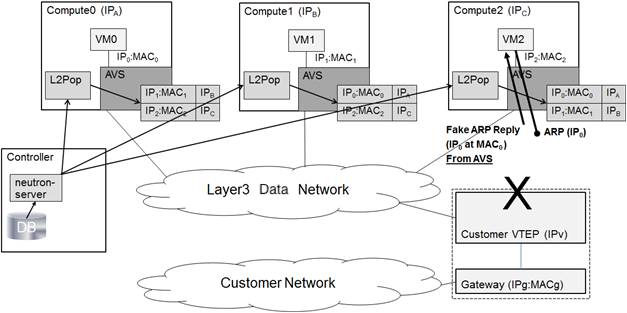
Static Endpoint Distribution¶
Note
In the static mode there is no dynamic endpoint learning. This means that if a node does not have an entry for some destination MAC address it will not create an entry even if it receives a packet from that device.
Workflow to Configure Static VXLAN Data Networks¶
Use the following workflow to create static VXLAN data networks and add segmentation ranges using the CLI.
Create a VXLAN data network, see Adding Data Networks Using the CLI.
Add segmentation ranges to static VXLAN data networks, see Adding Segmentation Ranges Using the CLI.
Establish routes between the hosts, see Adding and Maintaining Routes for a VXLAN Network.
For more information on the differences between the dynamic and static VXLAN modes, see Differences Between Dynamic and Static VXLAN Modes.
