Redundant Top-of-Rack Switch Deployment Considerations¶
For a system that uses link aggregation on some or all networks, you can configure redundant ToR switches for additional reliability.
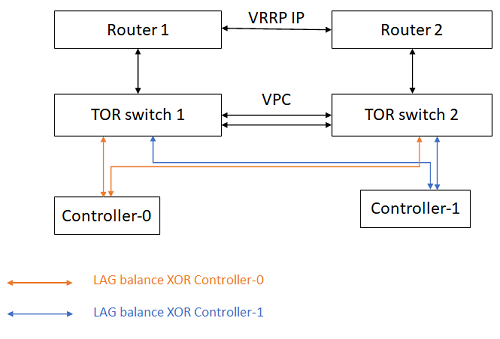
In a redundant ToR switch configuration, each link in a link aggregate is connected to a different switch, as shown in the accompanying figure. If one switch fails, another is available to service the link aggregate.
Redundant Top-of-Rack Switches¶
StarlingX recommends that you use switches that support VPC. When VPC is used, the aggregated links on the switches act as a single LAG interface. Both switches are normally active, providing full bandwidth to the LAG. If there are multiple failed links on both switches, at least one connection in each aggregate pair is still functional. If one switch fails, the other continues to provide connections for all LAG links that are operational on that switch. For more information about configuring VPC, refer to your switch documentation.
You can use an active/standby failover model for the switches, but at a cost to overall reliability. If there are multiple failed links on both switches, then the switch with the greatest number of functioning links is activated, but links on that switch could be in a failed state. In addition, when only one link in an aggregate is connected to an active switch, the LAG bandwidth is limited to the single link.
Note
You can enhance system reliability by using redundant routers. For more information, refer to your router documentation.
